What is stop limit price in forex? In the volatile forex market, precise control over your trades is paramount. The stop-limit order is a sophisticated instrument designed for this purpose, offering a blend of automation and control.
This guide will demystify its mechanics, benefits, and practical applications, showing you how to integrate this tool into your trading strategy.
Key takeaways:
- Definition: A stop-limit order in forex combines a stop price (triggers the order) and a limit price (controls execution price), offering precision but no execution guarantee.
- Components: Stop price activates the order; limit price ensures execution only at or better than the specified price, ideal for managing volatility.
- Types: Buy stop-limit (for entering uptrends above current price) and sell stop-limit (for selling on downtrends below current price).
- Benefits: Provides precise price control, automates trades, supports risk management, and suits strategies like breakouts or reversals.
- Risks: No execution guarantee due to price gaps or rapid market moves, complex for beginners, and may result in partial fills in low-liquidity markets.
- Comparison: Unlike stop-loss orders (guaranteed execution, less price control), stop-limit orders prioritize price precision over execution certainty.
- Practical use: Set on platforms like MetaTrader 4/5 or TradingView; requires testing on demo accounts and monitoring market conditions to avoid pitfalls.
- Strategic tips: Use wider stop-limit ranges, combine with technical analysis, and avoid high-volatility events to maximize effectiveness.
1. What is stop limit price in forex?
It refers to a trading order that uses two price points: a stop pr ice and a limit price. The stop price acts as a trigger when the market reaches this level, the order activates. Once triggered, it becomes a limit order, meaning it will only execute at the limit price or better.
For example, let's say you're watching the USD/CHF pair and want to enter a trade; you could set a stop price to trigger the trade and a limit price to ensure you don't pay more than you planned. This order type helps protect against sudden price swings in the forex market, which is known for its volatility.
Learn more in our full guide: What is a stop limit order.
Unlike a market order that executes immediately, a stop-limit order grants you tight control over the price range. This control, however, comes with a trade-off: execution is not guaranteed if the market moves too quickly. It is therefore an ideal tool for traders who prioritize precision over the certainty of a filled order.
To use a stop limit order effectively, you need to understand its two main parts: the stop price and the limit price. These components work together to define when and how your trade is executed. Here’s a breakdown:
| Component | Description | Example (Buy Order) |
|---|---|---|
| Stop price | The price that triggers the order | USD/CHF reaches 0.9500 |
| Limit price | The price range for execution | Buy at 0.9500 or lower |
- Stop price: This is the price level at which your order becomes active. For a buy order, it’s set above the current market price; for a sell order, it’s below.
- Limit price: This is the core component that provides control. It defines the absolute maximum price you are willing to pay (for buying) or the minimum price you will accept (for selling), ensuring your trade only executes within your specified range.
For instance, if USD/CHF is trading at 0.9450, you might set a buy stop price at 0.9500 and a limit price at 0.9510. If the market hits 0.9500, your order activates but only executes if the price is 0.9510 or lower. This structure helps beginners avoid unfavorable prices in volatile markets. The limit price on a stop order is what gives you this extra layer of control, making it a valuable tool for risk management.
2. How does stop limit price work?
A stop-limit order functions through two core components: a stop price to trigger the order and a limit price to define the execution boundary. The interplay between these two prices determines how the order behaves. There are two primary types to distinguish: the buy stop-limit and the sell stop-limit.
2.1. Buy stop limit order
A buy stop limit order is most effective when you anticipate a currency pair's price will break through a resistance level, and you want to enter the market once the uptrend is confirmed while still controlling your entry price.
The stop price is set above the current market price, and the limit price is equal to or higher than the stop price. Once the market hits the stop price, the order becomes a limit order, executing only at the limit price or lower.
Imagine you're analyzing the USD/CHF pair, currently trading at 0.9450. Your analysis suggests that if the price breaks through the key resistance level at 0.9500, it will continue to rise.
To catch this trend without chasing the price too high, you place a buy stop-limit order with a stop price at 0.9500 and a limit price at 0.9510. When the market hits 0.9500, your order is activated. However, the system will only execute the buy order if a price of 0.9510 or lower is available.
However, if the market jumps past 0.9510 due to volatility, your order may not execute. This makes buy stop limit orders ideal for disciplined traders who prioritize price control over guaranteed execution.
2.2. Sell stop limit order
Understanding the sell stop limit meaning in Forex is crucial for beginners, as a sell stop limit order is used to sell a currency pair when its price falls to or below a specific level, ensuring the trade executes at a predefined price or better.
The stop price is set below the current market price, and the limit price is equal to or lower than the stop price. When the market hits the stop price, the order becomes a limit order, executing only at the limit price or higher.
For instance, in a scenario where EUR/USD is trading at 1.1050, and you predict a decline if it drops below a support level at 1.1000. You place a sell stop limit order with a stop price of 1.1000 and a limit price of 1.0990. If the market falls to 1.1000, your order activates, but it will only sell if the price is 1.0990 or higher.
View more:
- Raw spreads vs no commission: Which forex account is better?
- What time frame is best for demand and supply indicator?
- What does NFP stand for? Definition and why it matters in finance – Expert’s insight
3. Why use stop limit price in forex trading?
Using a stop limit price in forex trading offers beginners a way to manage trades with precision and discipline. This tool is particularly valuable in the volatile forex market, where prices can change rapidly due to leverage and global events.
By combining a stop price and a limit price, traders can control when and how their trades execute. The decision to use a stop-limit order hinges on the trade-off between execution certainty and price control. This section will break down the specific benefits and inherent risks of the tool, helping you determine if it aligns with your trading approach.
3.1. Benefits of stop limit orders
Stop limit orders provide several advantages that make them appealing for beginners looking to navigate forex trading safely. They offer control and automation, which can reduce emotional decision-making. Here’s why traders use stop limit orders:
- Precise price control: The limit price on a stop order ensures you only trade at your desired price or better, avoiding costly executions in volatile markets.
- Risk management: By setting a stop price, you can limit potential losses or lock in profits.
- Automation: Once set, the order executes automatically when the stop price is reached, freeing you from constant market monitoring.
- Flexibility: Suitable for various strategies, such as trading breakouts or reversals, making it versatile for different market conditions.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Precise price control | Ensures trades execute at or better than your set limit price |
| Risk management | Limits losses or secures profits by triggering at the stop price |
| Automation | Executes without needing constant market watching |
| Flexibility | Works for breakout, reversal, or other trading strategies |
3.2. Risks of stop limit orders
While stop limit orders offer significant advantages, they also come with risks that beginners should understand. Knowing these challenges helps you use the tool wisely. Here are the key risks to consider:
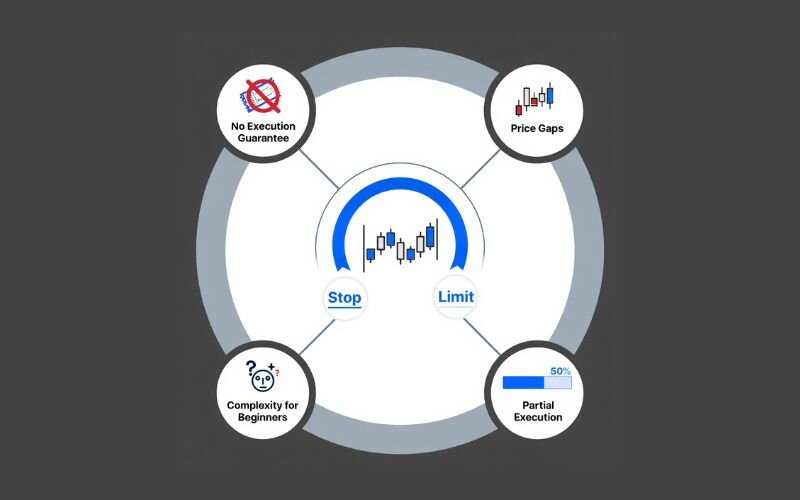
- No execution guarantee: If the market moves past your limit price too quickly, the order may not execute. This can lead to missed opportunities.
- Price gaps: Sudden market jumps, or gaps, can skip your limit price, leaving your order unfilled and exposing you to unexpected losses.
- Complexity for beginners: Setting both a stop and limit price can be confusing, requiring a clear understanding of market dynamics.
- Partial execution: In low-liquidity markets, only part of your order may execute, leaving the rest open to further price movements.
| Risk | Description |
|---|---|
| No execution guarantee | Order may not fill if market skips limit price |
| Price gaps | Sudden price jumps can prevent execution |
| Complexity | Requires understanding of stop and limit price settings |
| Partial execution | Only part of the order may execute in low-liquidity markets |
4. Stop limit vs. stop loss: What’s the difference?
One of the most common points of confusion for new traders is the difference between a stop-limit order and a stop-loss order. While both are risk management tools, they function in completely different ways and serve distinct purposes. Understanding this difference is key to using them correctly.
A stop limit order combines a stop price (to trigger the order) and a limit price (to control execution), offering precision but no guarantee of filling. In contrast, a stop loss order ensures execution by becoming a market order once the stop price is hit, but it sacrifices price control. Here’s a detailed comparison to clarify their roles:
| Feature | Stop limit order | Stop loss order |
|---|---|---|
| Execution type | Becomes a limit order | Becomes a market order |
| Price control | High (executes at limit price or better) | Low (executes at market price) |
| Execution guarantee | No (may not fill if limit price is missed) | Yes (fills at best available price) |
| Best for | Precision trading in stable markets | Quick exits in volatile markets |
For example, imagine trading USD/JPY at 145.00. You set a stop limit order to sell with a stop price of 144.50 and a limit price of 144.40. If the price drops to 144.50, the order activates but only executes at 144.40 or higher. If the market gaps to 144.30, your order won’t fill. With a stop loss order at 144.50, the trade would execute at the next available price, even if it’s 144.30, ensuring you exit but potentially at a worse price.
Stop limit orders, suit traders who prioritize price control, while stop loss orders are better for those needing guaranteed exits.
5. How to set a stop limit price on popular platforms
Setting a stop limit price in forex trading is straightforward once you understand the process on popular platforms. For beginners exploring what is the limit price on stop order, knowing how to implement it on tools like MetaTrader 4/5 or TradingView is essential.
These platforms are widely used for their user-friendly interfaces and robust features. This section provides step-by-step guidance on setting stop limit orders, helping you apply this tool confidently. Let’s dive into the practical steps for each platform.
5.1. Setting stop limit orders on MetaTrader 4/5
MetaTrader 4 and 5 (MT4/MT5) are among the most popular platforms for forex trading, offering easy access to stop limit orders. Here’s how to set one up:
- Open the platform: Launch MT4 or MT5 and log into your account.
- Select a currency pair: Choose a pair, like EUR/USD, from the Market Watch window.
- Open the order window: Right-click the pair, select “New Order,” and choose “Pending Order.”
- Choose stop limit order: From the order type dropdown, select “Buy Stop Limit” or “Sell Stop Limit.”
- Set stop and limit prices: Enter the stop price (to trigger the order) and the limit price (to control execution). For example, for a buy stop limit on EUR/USD at 1.1050, set a stop price of 1.1060 and a limit price of 1.1070.
- Confirm the order: Double-check your settings and click “Place” to activate the order.

The limit price on a stop order ensures your trade only executes within your specified range. Test this on a demo account first to avoid costly mistakes.
5.2. Using stop limit orders on TradingView
TradingView is a powerful charting platform that integrates with various brokers to place stop limit orders. While its interface differs from MT4/MT5, the process is intuitive. Here’s how to set a stop limit order:
- Access TradingView: Log into your TradingView account and select a currency pair, such as USD/JPY.
- Open the trading panel: Connect your broker account via TradingView’s trading panel.
- Select stop limit order: Click the “+” icon to open the order window, then choose “Stop Limit.”
- Enter stop and limit prices: Input the stop price to trigger the order and the limit price for execution. For instance, for a sell stop limit on USD/JPY at 145.00, set a stop price of 144.50 and a limit price of 144.40.
- Submit the order: Review your settings and confirm with your broker.
TradingView’s integration with brokers varies, so ensure your broker supports stop limit orders. This setup is ideal for traders seeking precision in volatile markets. For more on charting tools.
6. Practical tips for using stop limit price in forex
Understanding the theory is one thing; practical application is another. To use stop-limit orders effectively and avoid common pitfalls, traders should follow several strategic guidelines. These tips are designed to help you leverage the tool's strengths while mitigating its risks in the live market.
- Don't set your stop and limit prices too close together: One of the most common mistakes is setting a price range that is too narrow. The forex market is volatile, and a tight range can easily lead to your order never being executed. Give your order some "breathing room" by creating a reasonable buffer between the stop and limit prices.
For example, if USD/CHF is at 0.9450, setting a buy stop price at 0.9460 and a limit price at 0.9465 may be too narrow. Instead, allow a buffer, like a 10–15 pip range, to account for price fluctuations.
- Test on a demo account: Before using real funds, practice setting stop limit orders on a demo account. Platforms like MetaTrader 4/5 offer free demos to experiment with order types. This helps you understand how the limit price on a stop order works in real market conditions without financial risk.
- Monitor market conditions: Stay aware of economic events, like interest rate announcements, that can cause price gaps. Stop limit orders may not execute during sudden jumps.
- Use technical analysis: Combine stop limit orders with support and resistance levels to set smarter price points. For instance, place a buy stop limit order just above a resistance level for a breakout strategy.
- Review orders regularly: Market conditions change, so revisit your stop and limit prices periodically. Adjust them to reflect new trends or volatility to ensure they align with your trading goals.
7. Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Here are answers to some of the most common questions that traders have about stop-limit orders.
7.1. What is the difference between a stop limit price and a stop loss in forex?
A stop limit price combines a stop price (to trigger the order) and a limit price (to control execution), becoming a limit order when activated. In contrast, a stop loss order turns into a market order once the stop price is reached, ensuring execution but not price control.
For example, with EUR/USD at 1.1050, a stop limit order to sell at a stop price of 1.1000 and limit price of 1.0990 only executes at 1.0990 or higher, while a stop loss at 1.1000 sells at the next available price. Stop limit offers precision, but stop loss guarantees execution.
7.2. Can a stop limit order guarantee execution in forex trading?
No, a stop limit order does not guarantee execution. Once the stop price is reached, it becomes a limit order, only executing at the limit price or better. If the market moves too quickly or gaps past the limit price, the order may not fill.
For instance, if you set a sell stop limit on USD/JPY with a stop price of 144.50 and a limit price of 144.40, a gap to 144.30 could leave the order unfilled. Use stop limit orders when price control is more important than execution certainty.
7.3. How do I set a stop limit price on MetaTrader 4?
To set a stop limit price on MetaTrader 4 (MT4), open the platform, select a currency pair like GBP/USD, and right-click to open the “New Order” window. Choose “Pending Order,” then select “Buy Stop Limit” or “Sell Stop Limit.” Enter the stop price to trigger the order and the limit price to define the execution range.
For example, for a buy stop limit, set a stop price above the current price (e.g., 1.3000) and a limit price (e.g., 1.3010). Confirm by clicking “Place.”
7.4. When should I use a stop limit order in forex?
Use a stop limit order when you want precise control over your trade’s entry or exit price, especially in breakout or reversal strategies. For example, place a buy stop limit order above a resistance level to catch an upward breakout, or a sell stop limit to trade a downward break.
This order type is ideal for more stable markets or when trading pre-defined price zones, where controlling your entry price is more critical than guaranteeing execution. Be extremely cautious using them during high-impact news events, as the risk of the order not being filled is significant.
7.5. How does stop-limit price work?
It works by using a stop price to trigger the order and a limit price to set execution boundaries. Once triggered, the trade will only execute within the limit price range or better.
7.6. What is the stop-limit in forex?
It is an order type that lets traders automate execution while controlling the maximum or minimum price they’re willing to accept. It’s often used to trade breakouts or protect against slippage.
7.7. Should my stop price or limit price be higher?
For a buy stop-limit, the limit price is typically set slightly higher than the stop price. For a sell stop-limit, the limit price is usually set slightly lower than the stop price.
7.8. What is the 90% rule in forex?
It’s a trading concept suggesting that 90% of new forex traders lose 90% of their capital within the first 90 days. This emphasizes the importance of risk management and disciplined strategies.
Read more:
- What is a direct quotation? Clarifies its role in Forex
- Best support and resistance indicators for smarter trading
- Forex currency trading hours: What time does the forex market open?
8. Conclusion
Understanding what is stop limit price in forex is a vital step for beginners aiming to navigate the dynamic forex market with confidence. This tool, blending the precision of stop and limit orders, empowers you to manage risks and execute trades strategically.
At H2T Finance, we’re committed to providing educational blog content, tools, and strategies without pushing trading accounts, helping you build knowledge through neutral, high-value insights.
Whether you’re practicing on a demo account or exploring new strategies, stop limit orders can be a cornerstone of your trading journey. Continue your learning with our Forex Basics section, packed with beginner-friendly guides to boost your skills.



