Understanding how to trade the forex market is essential for anyone looking to navigate the world’s largest and most liquid financial marketplace. Forex trading offers vast opportunities but demands a solid grasp of strategies, tools, and risk management techniques to succeed.
This guide will provide you with clear, practical insights into trading forex, helping you build the foundation needed to make informed decisions. Whether you are a beginner or looking to refine your approach, mastering these essentials can greatly improve your trading confidence and outcomes.
Key takeaways:
- Forex trading involves buying one currency and selling another, aiming to profit from exchange rate movements.
- Understanding basic terminology (pip, lot, leverage, margin, bid/ask) is essential before entering the market.
- A structured 6-step process from choosing a pair to closing a trade helps build consistency and confidence.
- Platforms like MT4, MT5, and TradingView each offer unique strengths depending on trader style.
- Common strategies include trend-following, reversals, breakouts, and choosing between scalping, day trading, or swing trading.
- Risk management (stop-losses, take-profits, position sizing, emotional control) is the key to long-term survival.
- Practicing with demo accounts prepares traders before going live with real capital.
- Avoid beginner mistakes such as over-leveraging, ignoring stop-losses, and trading without a plan.
- Forex trading requires self-awareness assessing time, risk tolerance, and financial goals to decide if it’s the right fit.
1. What does it mean to trade the forex market?
Trading the forex market means buying one currency while simultaneously selling another, with the goal of profiting from changes in their exchange rate.
The foreign exchange (forex) market is the largest financial market in the world. According to the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) Triennial Survey in April 2022, the daily trading volume reached over $7.5 trillion, although this figure can fluctuate with market conditions.

Unlike stocks or commodities, forex trading focuses solely on currency pairs, such as EUR/USD or GBP/JPY.
When you learn how to trade the forex market, you're essentially speculating on whether the base currency (the first one in the pair) will strengthen or weaken against the quote currency (the second one). For example, if you believe the euro will rise against the US dollar, you'd go long (buy) on EUR/USD. If you think the euro will fall, you’d go short (sell) the pair.
Unlike investing, forex trading is typically short-term and fast-paced. It often involves using leverage borrowing capital from a broker to control larger positions. This can magnify both profits and losses, which is why risk management is critical when learning how to trade in the forex market.
The forex market is open 24 hours a day, five days a week, across major financial centers in London, New York, Tokyo, and Sydney. This global reach provides ample opportunity but also significant complexity.
Therefore, effective trading requires not only technical knowledge but also an awareness of economic events, central bank policies, and geopolitical risks that can affect currency prices.
2. Essential forex trading terminology (pip, lot, leverage, etc.)
Before you dive deeper, it’s important to understand the foundational terms used in trading. These concepts form the language of forex and will appear consistently as you analyze charts, place orders, and build strategies.

2.1. Pip
A pip (short for "percentage in point") is the smallest standard price movement in a currency pair. Most major pairs are priced to four decimal places, and a pip is typically the fourth digit after the decimal.
Example: If EUR/USD moves from 1.1050 to 1.1051, it has moved 1 pip.
2.2. Lot
A lot refers to the standardized size of a trade in forex.
- Standard lot = 100,000 units of the base currency
- Mini lot = 10,000 units
- Micro lot = 1,000 units
- Nano lot = 100 units
Lot size impacts the value of a pip and the potential gain or loss on a trade.
2.3. Leverage
Leverage allows traders to control a large position with a smaller amount of capital.
For example, with 50:1 leverage, you can trade $50,000 in currency with just $1,000 in margin.
Leverage can increase profits, but it also magnifies losses. If you're learning how to trade in the forex market, be cautious when using high leverage, especially as a beginner.
2.4. Margin
Margin is the capital required by your broker to open and maintain a leveraged position. It's not a fee, but rather a deposit held as collateral.
2.5. Bid and ask price
In the forex market, every transaction begins with two key prices: the bid and the ask. These are essential elements that determine how currencies are bought and sold. Understanding this concept not only helps you price trades accurately but also allows you to optimize your potential profits. So, what exactly are the bid and ask prices?
- The bid price is what buyers are willing to pay for a currency.
- The ask price is what sellers want in return.
- The spread is the difference between the two and represents the broker’s profit on the trade.
2.6. Base and quote currency
In any currency pair, the base currency is listed first (e.g., EUR in EUR/USD), and the quote currency is second (USD in EUR/USD). The exchange rate tells you how much of the quote currency is needed to buy one unit of the base.
Mastering these terms will be a solid foundation for your trading journey. Once you are fluent in the "language" of the market, you will be able to read trading platforms, understand price movements, and execute your decisions with confidence.
3. How to trade the forex market in 6 practical steps
If you're ready to get started, breaking down the trading process into manageable steps will help you build confidence and consistency. From choosing a currency pair to closing your position, below are 6 forex trading steps based on my years of experience and information from IG.
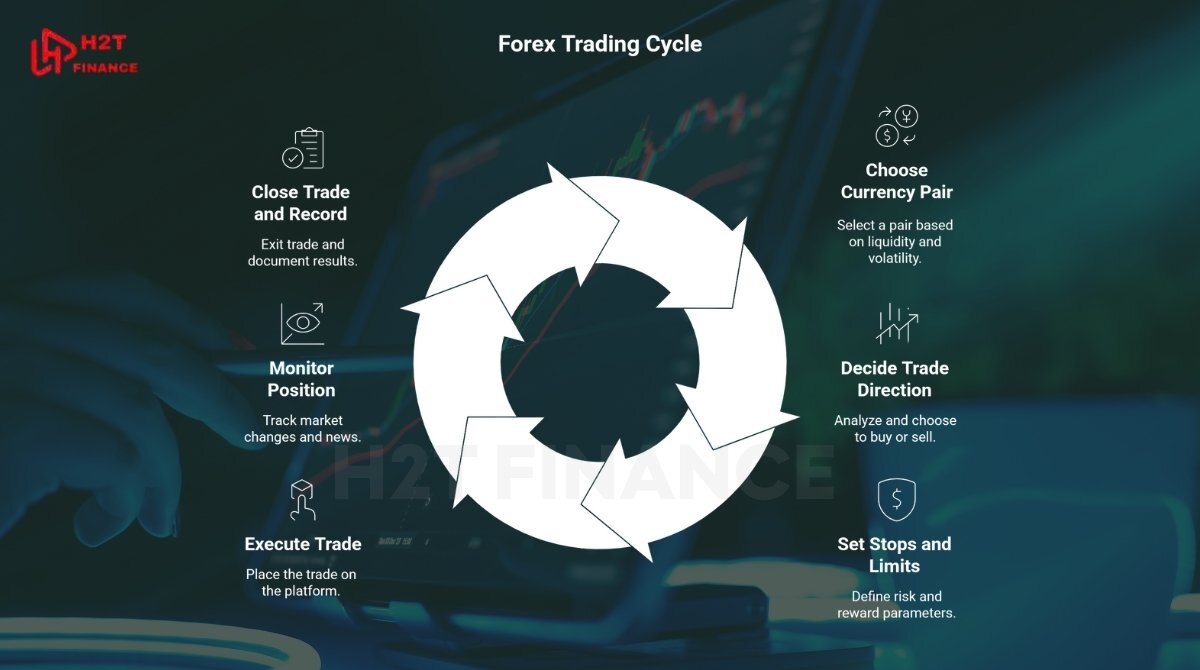
3.1. Choose a currency pair
Your first decision is selecting which currency pair to trade. Major pairs like EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY are popular for their liquidity and tighter spreads, while exotic pairs involve more risk but can offer greater volatility.
Before placing any trade, conduct:
- Fundamental analysis: Evaluate macroeconomic indicators like interest rates, inflation, GDP, and employment data from both countries.
- Technical analysis: Use price charts and indicators to spot patterns and trends.
Choosing the right pair depends on your strategy, market familiarity, and risk tolerance.
3.2. Decide whether to buy or sell
Once you've chosen a pair, the next step is deciding your trade direction based on your analysis:
- Buy (go long) if you believe the base currency will rise in value against the quote currency.
- Sell (go short) if you expect the base currency to fall.
For example, if GBP/USD is trading at 1.2800 and you believe the British pound will appreciate, you would go long. If you expect the pound to weaken, you'd go short.
Understanding price quotes is key when learning how to trade on the forex market. A quote of 1.2800 for GBP/USD means 1 GBP = 1.2800 USD.
3.3. Set your stops and limits
Forex trading is volatile, so protecting your position is crucial. Before opening a trade, define your risk and reward by setting:
- Stop-loss: Automatically closes your trade at a predetermined price to limit losses.
- Take-profit: Locks in your profits once a target price is hit.
- Trailing stop: Moves with favorable price action and protects gains without setting a fixed exit.
This is an essential part of risk management, especially when trading with leverage.
3.4. Execute the trade
Once you’ve selected your pair, decided on direction, and set your risk parameters, you’re ready to place your trade. On most platforms:
- Choose your trade size (lot size)
- Select 'buy' or 'sell'
- Confirm the order
Most brokers offer real-time quotes, fast execution, and options for market or pending orders.
3.5. Monitor your position
After opening a trade, actively monitor it. Price alerts and real-time charts can help you stay updated. Be aware of:
- Economic news: Central bank announcements or geopolitical events can move the market quickly.
- Spread widening: Especially during off-hours or major news releases.
- Swap fees: Charges for holding positions overnight.
Monitoring your trades ensures you stay in control and react to market changes appropriately.
3.6. Close the trade and record results
When your stop-loss or take-profit is triggered or when you decide to manually exit close your trade. It’s best practice to log every trade, including:
- Entry and exit points
- Rationale for the trade
- Outcome (profit or loss)
This helps you review your decisions and refine your strategy over time.
Learning how to trade in the forex market requires discipline, structure, and constant review. These steps create a repeatable routine you can adapt as you gain more experience.
4. Choosing the right forex trading platform (MT4 vs. MT5 vs. TradingView)
Selecting the right trading platform is a critical part of learning how to trade the forex market effectively. Your platform is where you’ll analyze charts, execute trades, and manage your strategy so it must align with your needs, experience level, and trading style.
Below is an overview of three of the most widely used platforms: MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), and TradingView.
4.1.. Overview and comparison of MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, and TradingView
Each platform offers distinct features and is suited to different types of traders. MT4 and MT5 are downloadable programs developed by MetaQuotes, while TradingView is a browser-based charting platform.
- MetaTrader 4 (MT4): Ideal for beginners and forex-focused traders. Known for its simplicity, stability, and broad broker support.
- MetaTrader 5 (MT5): Offers more advanced tools and access to additional markets (stocks, futures). Suitable for multi-asset traders and those needing built-in economic calendars.
- TradingView: A cloud-based charting platform favored for its modern interface, social community, and powerful technical analysis tools.
4.2. Table: feature comparison (technical indicators, ease of use, automation)
|
Feature |
MT4 |
MT5 |
TradingView |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Interface |
Basic, stable |
More modern than MT4 |
Intuitive, web-based |
|
Technical Indicators |
~30 built-in + custom |
~38 built-in + custom |
100+ built-in + community scripts |
|
Chart Types |
Line, bar, candlestick |
Line, bar, candlestick |
Multiple + advanced customization |
|
Automation |
Yes (via Expert Advisors) |
Yes (multi-threaded EAs) |
Limited (via Pine Script) |
|
Backtesting |
Single-threaded |
Multi-threaded & faster |
Limited |
|
Assets Available |
Forex |
Forex + stocks + more |
All global markets (charting only) |
|
Community/Social |
Limited |
Limited |
Strong social trading features |
|
Installation |
Desktop/mobile only |
Desktop/mobile only |
Web + mobile + desktop app |
|
Cost |
Free via broker |
Free via broker |
Free + paid plans |
4.3. Platform recommendations based on trading style
When choosing how to trade in the forex market, matching your platform to your trading strategy can boost efficiency and comfort.
- Scalpers and day traders often prefer MT4 for its speed and direct broker integration.
- Advanced traders who want access to stocks, futures, and better backtesting might opt for MT5.
- Chart-focused traders or those who enjoy scripting indicators and sharing ideas with a trading community tend to lean toward TradingView.
If you’re still learning how to trade on the forex market, you might want to experiment with demo accounts on each platform to see which interface suits your workflow best.
5. Common forex trading strategies that work
If tools and platforms are your vehicle, then strategy is your roadmap. There is no "holy grail" or secret formula that guarantees a win every time. Instead, a successful trader finds an approach that resonates with their personality, goals, and even their daily schedule. Let's explore a few popular schools of thought that have been tested by generations of traders.
These strategies can be combined with technical indicators and sound risk management to help you trade with more confidence whether you're trading intraday, swing, or long term.
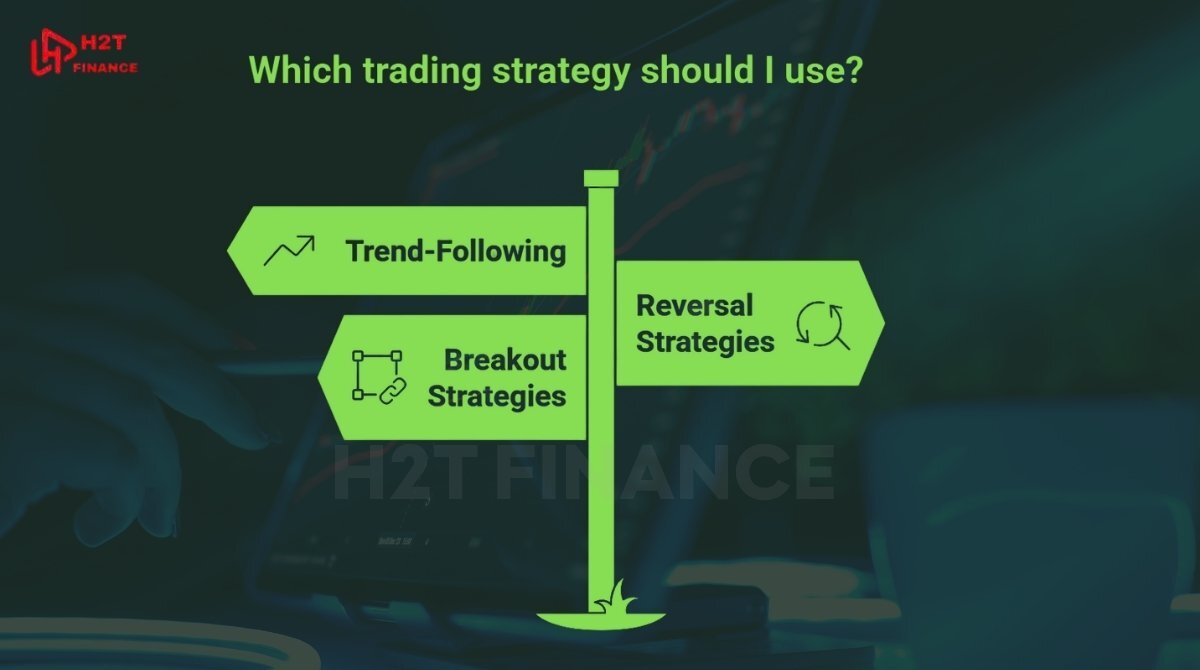
5.1. Trend-following strategies (e.g., moving average cross)
Trend-following is one of the most beginner-friendly and effective strategies. The goal is to "ride the trend" rather than predict reversals.
Popular technique: Moving Average Crossovers
- When a short-term moving average (e.g., 50 EMA) crosses above a longer-term one (e.g., 200 EMA), it may signal a bullish trend.
- The opposite suggests a downtrend.
Pros:
- Works well in trending markets.
- Easy to implement with MT4 or TradingView indicators.
Cons:
-
Generates false signals in sideways markets.
This strategy is especially useful for beginners who want to avoid overcomplicating their setup.
5.2. Reversal strategies (e.g., double top/bottom, RSI divergence)
Reversal strategies aim to catch turning points in the market ideal for traders who prefer precision and shorter-term trades.
Examples:
- Double Top/Bottom: Classic chart patterns signaling trend exhaustion.
- RSI Divergence: When price forms a new high but RSI doesn’t, it may indicate a reversal is near.
Caution: Reversals carry more risk. They require good timing, confirmation, and strict stop-losses.
5.3. Breakout strategies
Breakout trading focuses on price movements that escape consolidation zones or key support/resistance levels.
How it works:
- Identify a range or pattern (e.g., triangle, rectangle).
- Enter when price breaks out with volume.
Breakouts often lead to strong momentum moves, especially around news events or market opens. This strategy works well with TradingView alerts or MT5’s built-in breakout indicators.
5.4. Scalping, day trading, swing trading explained
Your preferred trading timeframe can help determine the strategy you choose. Here’s how they differ:
|
Strategy |
Timeframe |
Trade Duration |
Suitable For |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Scalping |
1–5 minute charts |
Seconds to minutes |
Fast decision-makers, low spreads |
|
Day Trading |
5–30 minute charts |
Minutes to hours |
Full-time or part-time traders |
|
Swing Trading |
1H–4H–Daily charts |
Days to weeks |
Those balancing trading with other tasks |
If you're just starting to learn how to trade the forex market, swing trading often provides a healthy balance between flexibility and analysis depth.
5.5. How to choose a strategy based on personality and schedule
When deciding how to trade on the forex market, your trading strategy should fit your lifestyle and emotional tendencies. Ask yourself:
- Are you patient or impulsive?
- Can you monitor trades during the day?
- Do you prefer quick wins or long-term trends?
Tip: Backtest different strategies using demo accounts to see what aligns best with your routine and psychology. Don’t force a strategy just because it works for others consistency and comfort matter more in the long run.
6. Managing risk in forex trading
Think of it this way: a good strategy might help you make profits, but it's risk management that keeps you in the game. This is the core element that separates professional traders from the rest of the crowd.
It helps you survive losing streaks, reduce emotional decision-making, and grow your account steadily over time.
This section covers essential risk management concepts that every forex trader should understand and apply.
6.1. What is risk management in forex?
Risk management refers to the process of identifying, assessing, and minimizing the financial risks associated with trading. In forex, this often means:
- Controlling how much capital is exposed per trade.
- Defining your acceptable loss before entering a position.
- Applying consistent rules regardless of market emotions.
Without risk management, even the best trading strategy can lead to failure especially in the highly leveraged forex market.
6.2. Types of orders: stop-loss, trailing stop, take-profit
Using the right types of orders is critical in protecting your account from unexpected market moves.
- Stop-loss: Closes your trade automatically when a set loss level is reached. It limits how much you can lose if the trade goes against you.
- Take-profit: Closes the trade when your profit target is hit. This locks in gains before the market reverses.
- Trailing stop: Adjusts automatically as the market moves in your favor, securing profits while allowing room for growth.
These orders are available on MT4, MT5, and TradingView-compatible brokers, making them easy to use even if you're just starting to learn how to trade on the forex market.
6.3. Position sizing and leverage management
Trading forex with leverage can amplify both gains and losses. That’s why position sizing and leverage control are crucial components of risk management.
Key tips:
- Never risk more than 1–2% of your account balance on a single trade.
- Use a position size calculator to match lot size with stop-loss distance and account risk.
- Avoid high leverage unless you have fully mastered your risk management strategy. Remember that leverage not only magnifies potential profits but also magnifies corresponding losses, which can wipe out your account with just a small market fluctuation.
Trading safely means respecting leverage treat it as a tool, not a shortcut.
6.4. Psychology of losses: how to stay rational
The emotional side of trading is just as important as technical skill. Losing trades can trigger fear, anger, or revenge trading all of which can lead to irrational decisions.
Mindset tips:
- Accept that losses are part of the game no strategy wins 100% of the time.
- Stick to your trading plan and avoid emotional overreactions.
- Take breaks if needed. Overtrading often leads to poor performance.
To succeed in forex, you must develop emotional discipline. The best traders are not those who win the most they’re the ones who manage their losses best.
7. How to practice forex trading without risk
Every complex skill needs to be practiced in a safe environment before being applied in the real world. In the world of forex, that environment is the demo account. It's the perfect training ground a risk-free setting where you can build muscle memory, test-drive your strategies, and master your trading platform before you put real capital on the line.
7.1. Demo accounts: what they are and how to use them effectively
A demo account simulates live forex trading using virtual funds. It allows you to trade currency pairs under real market conditions just without the emotional pressure of losing actual money.
How to use a demo account effectively:
- Treat it like real money: Follow your trading plan as if your capital were on the line.
- Practice using technical tools: Apply indicators, draw trendlines, and place different types of orders.
- Use it to master your platform: Whether you're using MT4, MT5, or TradingView, become fluent in navigating the interface.
Demo accounts are available from nearly all brokers and trading platforms, and they’re essential for anyone looking to learn to trade properly.
7.2. Common mistakes traders make in demo vs. live trading
While demo trading is invaluable, it has one major limitation: emotions are not involved. When your money isn’t at stake, it’s easier to take risky trades or ignore rules.
Common mistakes include:
- Overtrading because losses don’t “hurt”
- Taking unrealistic position sizes
- Not tracking performance or refining strategy
- Building overconfidence that doesn’t translate into live trading
Being aware of these differences will help you transition more smoothly when you move from demo to real trading.
7.3. How long to use a demo before going live
There’s no perfect timeline, but most experts recommend demo trading for at least 1 to 3 months, depending on your background and strategy complexity.
Consider going live when:
- You have a consistent strategy with clear rules
- You’ve tested it across different market conditions
- Your demo results show stable performance over a large number of trades (e.g., 50+)
Even after going live, you can continue to use your demo account to test new ideas or tools without risking real money.
8. Common mistakes beginners make when trading forex
Let's be honest with each other: every professional trader you admire today was once a beginner, and they all made mistakes. Those first stumbles aren't signs of failure; they are valuable "tuition fees" paid on the path to growth. By identifying these common pitfalls in advance, you can shorten your learning curve and better protect your account.

8.1. Over-leveraging
Leverage can be both a blessing and a curse. Many beginners are tempted by the potential for large profits and use the maximum leverage allowed by their broker.
Why it’s a mistake:
- Higher leverage increases both gains and losses.
- Even small market movements can wipe out your account if you over-leverage.
- It encourages gambling behavior rather than strategic trading.
Tip: Start with low leverage (e.g., 10:1 or 20:1), and focus on risk-adjusted returns, not just big wins.
8.2. Ignoring stop-losses
Some traders avoid setting stop-losses, believing they’ll “watch the trade” and close it manually. In reality, emotions and market speed can make this impossible.
Why it’s a mistake:
- You can lose far more than planned.
- Unexpected news events can move the market in seconds.
- Manual exits require discipline that many beginners lack.
Tip: Always set a stop-loss based on your strategy. Think of it as an essential insurance policy for your trade.
8.3. Trading without a plan
Jumping into trades without a defined strategy is like sailing without a map you’re likely to get lost quickly.
Why it’s a mistake:
- Leads to impulsive, inconsistent decisions
- Makes it hard to measure performance or improve
- Often results in emotional trading
Tip: Develop a trading plan with clear entry, exit, and risk rules. Use your demo account to refine it before going live.
8.4. Chasing the market or revenge trading
It’s common for new traders to feel the urge to win back losses immediately or jump into trades just because the market is moving fast.
Why it’s a mistake:
- These behaviors are driven by emotion, not logic.
- Often leads to bigger losses and account blowups.
- Makes you lose control over your system and rules.
Tip: Take a break after a losing trade. Review what went wrong and return only when you’re calm and objective.
9. Is forex trading right for you?
Before you embark on this exciting journey, it’s time for an honest check-in. Forex trading isn't a one-size-fits-all path; it's a commitment that needs to align with who you are. This section is designed to help you "look in the mirror" and ask the important questions about your time, risk appetite, and financial goals to see if this world is truly the right fit for you.
9.1. Assessing your time, risk tolerance, and financial goals
Forex trading requires consistent time commitment, especially if you plan to use active strategies like day trading or scalping.
- Time: Do you have hours daily or weekly to study markets, analyze charts, and monitor trades?
- Risk tolerance: Are you comfortable with potential losses, which can be significant due to leverage?
- Financial goals: Are you seeking short-term profits, long-term wealth growth, or supplemental income?
Honest answers to these questions help you choose an approach that fits you, or decide if forex trading is right at all.
9.2. Comparing trading vs. investing mindset
Trading typically means frequent buying and selling to profit from price fluctuations. This approach requires discipline, emotional control, and a strategic mindset.
Investing, on the other hand, is usually longer term, focusing on fundamental value and steady growth.
Knowing which mindset suits you best helps tailor your forex activities or consider other financial markets instead.
9.3. When to avoid forex trading
Forex trading may not be suitable if:
- You cannot afford to lose the money you invest.
- You lack time to learn and practice consistently.
- You have a low tolerance for stress or volatility.
- You’re easily influenced by hype, rumors, or emotion.
It's critical to be honest about one thing: a vast majority of retail traders lose money, especially in the beginning. Therefore, thorough preparation and realistic expectations are essential for survival.
Explore more trading insights:
- What is contract size in Forex? Beginner’s guide
- What was the purpose of this trading pattern? Full explain
- Step-by-step guidehow to save indicators on sway markets
10. Related questions about forex trading (FAQs)
When learning how to trade the forex market, it’s normal to have many questions. Below, we answer some of the most common ones to help you deepen your understanding.
10.1. Can I start forex trading with $100?
Yes, many brokers allow you to open accounts with as little as $100. However, starting with a small amount means you’ll need to use leverage carefully and set realistic profit expectations. Using a demo account to practice before risking real money is always recommended.
10.2. How do forex brokers make money?
Forex brokers typically earn money through the spread - the difference between the bid and ask prices. Some brokers may also charge commissions or fees on trades or overnight financing fees (swap rates).
10.3. How much money can you make trading forex?
Potential profits vary widely depending on your capital, strategy, risk management, and market conditions. Forex trading can be profitable but also involves significant risks. Many beginners lose money, so realistic expectations and education are essential.
10.4. What are the best currency pairs to trade?
The most popular pairs are majors such as EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, USD/CHF, AUD/USD, and USD/CAD due to their liquidity and tight spreads. These pairs usually offer more stable trading conditions than exotic pairs.
11. Conclusion: Mastering how to trade the forex market takes time
Learning how to trade the forex market is a journey that requires both knowledge and self-awareness. From mastering terminology and platforms to building strategies and managing risk, every step contributes to your success as a trader.. In summary, the key takeaways you should remember include:
- Solid foundation: Master the basic terminology and principles of the market.
- Clear strategy: Build a trading plan that aligns with your goals and style.
- Disciplined risk management: Always prioritize capital protection with stop-losses and proper position sizing.
- Practice and learning: Utilize a demo account and constantly analyze to improve your skills.
Forex trading isn’t a guaranteed way to get rich quickly. But with preparation, structure, and the right mindset, it can become a powerful tool for financial growth. If you're still deciding how to trade the forex market, start small, stay consistent, and never stop learning.
Ready to go deeper? Explore more beginner-friendly guides and insights in our Forex Basics by H2T Finance.
Have you started trading forex yet? What’s been your biggest challenge so far? Feel free to leave a comment or question below we’d love to hear from you.



