In the fast-paced world of forex trading, every decision you make carries potential gains and risks. This is why understanding the formula for risk reward ratio and applying the formula for risk ratio in forex is essential. It helps you quantify the balance between how much you're willing to risk and how much you expect to gain.
In this article, H2T Finance will walk you through the concept, how it works, and how to use it practically, backed by insights from real trading scenarios.
Key takeaways:
- The risk/reward ratio (RRR) measures potential loss compared to potential gain, helping traders decide if a trade is worth taking.
- A common formula: RRR = (Entry Price – Stop-Loss) ÷ (Take-Profit – Entry Price).
- Popular benchmarks: 1:2 or 1:3 ratios allow profitability even with win rates below 50%.
- Using stop-loss and take-profit levels is essential for consistent risk management.
- The “best” ratio depends on strategy: scalpers may use 1:1, while swing traders often aim for 1:3+.
- A disciplined RRR strategy reduces emotional trading and supports long-term growth.
- Tools like TradingView, MetaTrader plugins, and online calculators make applying the formula easier.
- Avoid common mistakes: chasing unrealistic RRRs, ignoring trading costs, or misplacing stop-loss orders.
1. What is a risk ratio? Definition in a financial context
The risk ratio, also known as the risk/reward ratio or risk/return ratio, measures how much an investor stands to lose relative to the potential reward of an investment. It is a critical component of risk management, used to evaluate whether an investment is worth pursuing.
How about we illustrate this with a practical example? If you're considering a forex trade where your potential loss is $100 and your expected gain is $300, your risk/reward ratio is 1:3. That means for every dollar you're willing to lose, there's a potential to gain three. Conversely, a 1:1 ratio means the potential profit equals the risk, which might not be attractive in volatile markets.
The risk ratio shows potential loss compared to potential reward in an investment. The risk ratio shows potential loss compared to potential reward in an investment
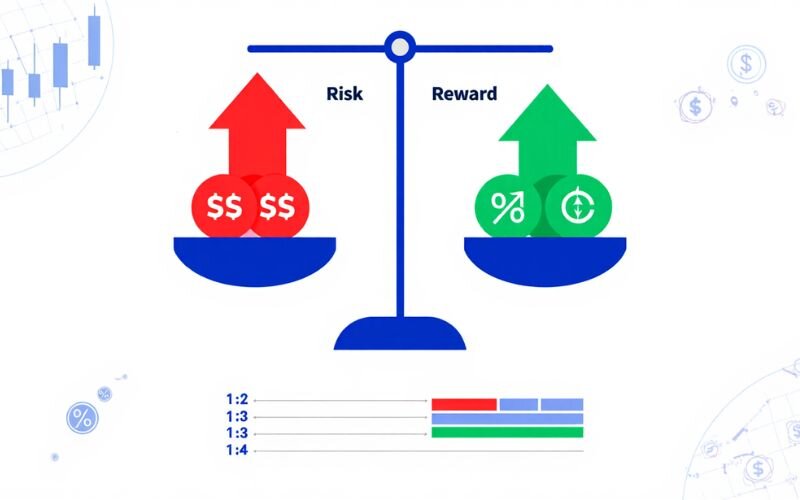
In practice, traders use this ratio to decide:
- Deciding if a trade is worth taking or better left alone.
- Determining the optimal points for stop-loss and take-profit.
By embedding the formula for risk ratio into every trading decision, you gain a powerful filter that protects your capital from emotionally driven mistakes.
Example:
You plan to enter a trade on GBP/USD at 1.2500.
- You set a stop-loss at 1.2450, risking 50 pips.
- Your take-profit is at 1.2600, aiming for 100 pips gain.
Your risk-reward ratio is:
Risk = 50 pips, Reward = 100 pips → RRR = 1:2
This means you’re risking 1 pip to potentially gain 2 pips—a favorable setup that many traders would consider worth taking.
2. How does the risk ratio work?
Understanding how the risk ratio works means understanding both sides of a trade: the risk (how much you could lose) and the reward (how much you could gain). This concept lies at the heart of trading psychology and portfolio protection.
Professional traders often target a 1:3 risk-reward ratio, meaning they aim to gain $3 for every $1 they risk. However, the optimal ratio can vary based on trading strategy. Scalpers may use lower ratios like 1:1.2 due to shorter trade durations, while swing traders might aim for 1:4 or more to capture larger market moves.
If you're new to the concept, you're probably wondering: how to calculate risk ratio in forex? It starts with identifying your:
- Entry price
- Stop-loss level (how much you're willing to lose)
- Take-profit level (your expected profit target)
The formula is simple:
Risk-Reward Ratio = (Entry Price - Stop-Loss) / (Take-Profit - Entry Price)
Let’s say you buy EUR/USD at 1.1000, set your stop-loss at 1.0950 (50 pips risk), and your take-profit at 1.1150 (150 pips gain). The calculation is:
Risk-Reward Ratio = 50 / 150 = 1:3
That means you risk 1 pip for every 3 pips of potential gain. Understanding how to calculate risk ratio in forex like this allows you to assess the quality of every trade before execution.
To manage risk more effectively, investors rely on tools like:
- Stop-loss orders: Automatically close a trade at a preset loss level.
- Take-profit orders: Lock in gains once the asset hits a specific price.
- Technical or fundamental analysis: Estimate expected returns and potential drawdowns using price charts, news events, or financial statements.
Some traders also incorporate advanced models like CAPM (Capital Asset Pricing Model) or Value-at-Risk (VaR) to strengthen their risk analysis. The more data-driven your method, the more reliable your risk/reward ratio estimations will be.
Ultimately, understanding how to calculate the risk ratio in forex is not just about math—it's about creating a structured decision-making process that reduces emotional trading and increases consistency. The formula for risk ratio turns uncertainty into a measurable advantage.
3. Best risk to reward ratio in Forex
There is no universal “perfect” risk to reward ratio that fits all traders, but some ratios have proven to be more effective depending on the trading style and market conditions. Most professional forex traders aim for a risk-reward ratio of at least 1:2, meaning they seek to gain $2 for every $1 they risk. This creates a margin of safety—even if you win only 40% of your trades, you can still be profitable.
Here’s a quick comparison of commonly used ratios:
| Risk-Reward Ratio | Win Rate Needed to Break Even | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| 1:1 | Over 50% | Scalping, fast trades |
| 1:2 | ~40% | Day & swing trading |
| 1:3 | ~33% | Trend-following setups |
| 1:4+ | Below 30% | High-confidence, long-term setups |
While a higher ratio (like 1:4 or more) may seem attractive, it usually comes with a lower probability of success. Therefore, the best risk to reward ratio in Forex is the one that complements your trading strategy, time frame, and risk tolerance.

It’s also crucial to evaluate each trade’s context—tight spreads, volatility, market structure, and realistic price movement must all be considered before deciding on a target ratio. Most importantly, your chosen ratio should be one you can apply consistently and with discipline.
4. Why is the risk ratio important for forex traders?
The forex market is naturally prone to frequent price swings. Without a framework like the risk ratio, it's easy to fall into the trap of emotional or revenge trading. Here’s how mastering this formula improves your trading:
- Risk Management: Helps limit large losses and preserve capital. For instance, even with a 50% win rate, a 1:2 risk/reward ratio means you're profitable over time.
- Objective Decision-Making: Keeps you grounded. You’re no longer swayed by a hunch or market noise.
- Consistency: Following a fixed RRR (Risk-Reward Ratio) strategy helps make outcomes more predictable and trading behavior more disciplined.
A good practice is to calculate your average RRR and refine it based on performance. For example, I found that adjusting from a 1:2 to a 1:2.5 ratio significantly reduced losses during high-volatility sessions in the London market.
Additionally, remember to include trading costs (like spreads and commissions) in your calculations, they can skew your actual reward.
5. What is a formula for risk ratio? The risk ratio formula explained by experts
It’s relatively simple to figure out the formula for risk reward ratio, a key concept in risk management. Here’s the basic formula for risk ratio in forex and how to apply it before every trade.
Risk/Reward Ratio = Potential Loss / Potential Gain
Another variation you could encounter is:
RRR = (Entry Price - Stop-Loss) / (Take-Profit - Entry Price)
For example:
- Entry Price = 1.1000
- Stop-Loss = 1.0950 (risking 50 pips)
- Take-Profit = 1.1150 (expecting 150 pips)
Then, Risk/Reward Ratio = 50 / 150 = 1:3
This means you're risking 1 pip for every 3 pips of potential gain. Ideally, you'd only take trades that align with your target RRR threshold, whether it’s 1:2, 1:3, or higher.
By applying this formula before every trade, you prevent overexposure and stay aligned with long-term profitability goals.
See more related articles:
- What is a binary option? How they work & key risks
- Forex currency trading hours: What time does the forex market open?
- Floating currency exchange rate explained for Forex implications
6. Expert guide: How to calculate your risk ratio before a trade - Step-by-step using the formula for risk ratio
One of the most powerful tools in a trader's arsenal is understanding and applying the formula for risk ratio effectively. Knowing how to calculate your risk ratio before every trade could be the single most important step toward consistent profitability. Let’s unpack this in clear, manageable steps.
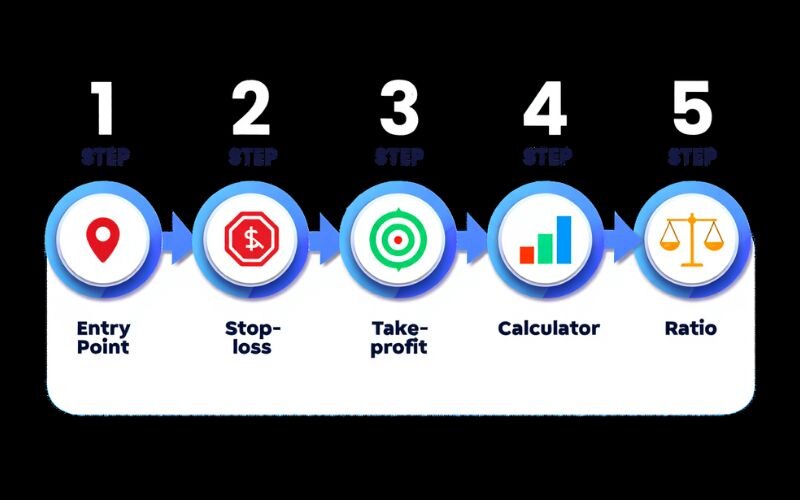
6.1. Step 1: Define your entry point
Every trade begins with a plan, and that plan must start with a well-thought-out entry point. This is the price level where you decide to enter the market, typically based on technical or fundamental analysis.
Real example: Suppose you've analyzed the EUR/USD pair and believe it’ll rise from the current market structure. You plan to buy at 1.1200, this is your entry point. Based on patterns, moving averages, or Fibonacci retracement levels, this decision should not be random.
6.2. Step 2: Set your stop-loss level
Now that you’ve chosen your entry, it’s time to protect your capital. The stop-loss level is a key part of the formula for risk ratio because it determines your maximum loss if the trade goes against you.
Example: you’re only willing to lose 50 pips on this trade. You place your stop-loss at 1.1150. This safety net prevents devastating losses and is critical for long-term survival in trading.
6.3. Step 3: Determine your take-profit level
Equally important is your take-profit level. This is where you plan to exit the trade if the market moves in your favor. It's not just about hoping for a gain, it’s a calculated decision based on realistic price targets.
Example: If your take-profit is set at 1.1300, you’re aiming to make 100 pips from this move. This gives structure to your trade and sets expectations.
6.4. Step 4: Calculate potential loss and profit
Let’s get into the numbers, where the risk ratio formula begins to take shape.
- Potential Loss = Entry Point - Stop Loss Level
= 1.1200 - 1.1150 = 50 pips
- Potential Profit = Take Profit Level - Entry Point
= 1.1300 - 1.1200 = 100 pips
These figures are not just for records, they fuel your decision-making process. Calculating your pip value based on position size would further fine-tune this.
6.5. Step 5: Calculate the risk-reward ratio
Now, apply the core formula for risk ratio:
Risk Reward Ratio (RRR) = Potential Profit / Potential Loss
RRR = 100 / 50 = 2
This means you’re risking 1 pip to gain 2 pips, a 1:2 ratio. It’s a positive ratio, signaling a favorable setup. Most seasoned traders aim for ratios above 1:1, though this depends on strategy and market conditions.
7. Example: Formula for risk ratio in use
Let’s expand on this with a broader Forex context. Imagine you have:
- Take Profit Price – 0.94193
- Entry Price – 0.90021
- Stop Loss Price – 0.88020
So, how to calculate risk ratio in trading?
Risk Reward Ratio (Long Position) = (Entry - Stop Loss) / (Take Profit - Entry)
= (0.90021 - 0.88020) / (0.94193 - 0.90021)
= 0.02001 / 0.04172 ≈ 1:2.08
So, for every dollar you risk, you stand to gain $2.08. This aligns with a disciplined trading approach.
8. Ideal risk ratio: What ratio should you aim for?
So, what is a good risk ratio? There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. A risk-reward ratio of 1:1 requires a win rate of over 50% just to break even. A 1:2 ratio offers a buffer; even if you're right only 40% of the time, you can still be profitable.
Quick breakdown:
- 1:1 ratio → Need >50% success rate.
- 1:2 ratio → Profitable even with ~40% win rate.
- 1:3 or higher → Fewer wins needed, but harder to reach targets.
Set realistic goals. Day traders might stick to 1:1 or 1:2 due to tight price ranges, while swing or position traders can aim higher. It all depends on your style, time horizon, and market conditions.
Before entering any trade, use the formula for risk ratio to assess whether your target is achievable. Always ask: Can this trade realistically reach the profit target before hitting the stop-loss? If not, skip it.
9. Common mistakes when using the risk ratio that investors should know
While the risk/reward ratio is simple in theory, many traders misuse or misinterpret it. Here are the common pitfalls:
- Chasing High RRR Without Realism: Aiming for 5:1 sounds attractive but may be unachievable due to market volatility or spread costs.
- Setting Unrealistic Stop-Losses: Forcing a tighter stop just to improve your ratio can result in getting stopped out frequently.
- Ignoring Hidden Costs: Not factoring in slippage, commissions, and spreads can give you a misleading RRR.
- Sticking to RRR Dogmatically: A ratio that works in trending markets might fail in choppy ones. Adapt your RRR based on market context.
For example, when I traded EUR/USD during high-impact news releases, my tight 1:3 strategy led to constant stop-outs due to sudden spikes. Switching to a wider stop and a more modest 1:2 ratio improved results instantly.
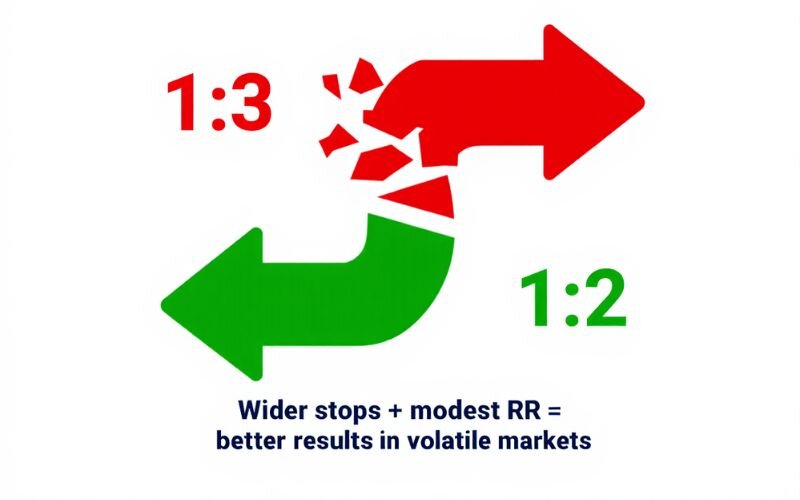
This experience reinforced the importance of adapting the formula for risk ratio to real market conditions. Remember: The best risk ratio is the one you can execute consistently and profitably.
10. Experts' tips: Tools to help you calculate risk ratio automatically
To make life easier, here’s a handy table of tools that simplify your risk ratio calculations:
| Tool / Platform | Features | Platform Type |
|---|---|---|
| TradingView | Built-in risk-reward drawing tool, chart integration | Web / Desktop / Mobile |
| Myfxbook | Free position size calculator, RRR calculator | Web |
| MetaTrader Plugin | Risk calculator plugins for MT4/MT5 | Desktop (MetaTrader) |
| ThinkorSwim Plugin | Custom scripts & strategies for RRR | Desktop (ThinkorSwim) |
| Forex Calculators | Websites like BabyPips, DailyFX offer calculators for risk-reward | Web |
| Mobile Apps | Tools like Stinu or Forex Risk Calculator for on-the-go analysis | iOS / Android |
Using these tools ensures speed, accuracy, and consistency in your calculations.
11. FAQs: Common questions when searching for the formula for risk ratio
11.1. How often should I recalculate the formula for risk ratio in my trading?
You should recalculate it before every trade and periodically review your overall average ratio to adapt to changing market conditions and personal performance.
11.2. Can the formula for risk ratio help with money management beyond entry and exit points?
Absolutely. It’s a key part of position sizing and portfolio risk control, helping you decide how much capital to allocate per trade for consistent growth.
11.3. Can beginners rely solely on the formula for risk ratio?
While it’s a crucial tool, beginners should combine it with solid education, demo trading, and understanding market context to build confidence and avoid mistakes.
11.4. What role does psychology play in following the formula for risk ratio?
Maintaining self-control and staying focused is key to long-term success. Sticking to your calculated risk ratio prevents impulsive decisions driven by fear or greed.
11.5. How does leverage impact the formula for risk ratio?
Leverage can increase potential gains as well as losses. Even with a good risk ratio, improper leverage can lead to large losses, so use leverage cautiously.
11.6. What is a 1 to 2 risk-reward ratio in forex?
A 1:2 risk-reward ratio means you are risking 1 unit of capital (e.g., $100) to potentially gain 2 units (e.g., $200). In pip terms, if your stop-loss is set at 50 pips, your take-profit should be 100 pips. This ratio implies that even if you win only 50% of your trades, you can still be profitable over time. It’s a common target for swing and position traders aiming for solid returns without excessive risk.
11.7. What is the 2% rule in forex?
The 2% rule is a widely used risk management principle stating that you should not risk more than 2% of your total account balance on a single trade. For example, if your account has $5,000, the maximum loss you should allow per trade is $100.
This rule helps protect your capital from large drawdowns and supports long-term trading sustainability. When combined with a favorable formula for risk reward ratio, it enhances your ability to manage losses and grow steadily.
11.8. How is risk ratio calculated?
Risk ratio is calculated as potential loss ÷ potential gain. In trading, this is often expressed as stop-loss distance over take-profit distance, e.g., 50 pips loss vs 100 pips gain = 1:2.
11.9. How to calculate 95% CI for risk ratio?
In statistics or medical studies, the 95% confidence interval (CI) for a risk ratio is usually derived using the natural log of the ratio and its standard error. The CI shows the range within which the true risk ratio is likely to fall with 95% confidence.
11.10. When to use HR vs RR?
- RR (Risk Ratio): Used in clinical trials, investments, or trading to compare probabilities or risks directly.
- HR (Hazard Ratio): Common in survival analysis or medical research, showing the rate of an event occurring over time.
In trading, RR is relevant, not HR.
11.11. How to calculate risk ratio trading?
In trading, the formula is: Risk/Reward Ratio = (Entry – Stop Loss) ÷ (Take Profit – Entry).
Example: Buy EUR/USD at 1.1000, stop-loss 1.0950 (50 pips risk), take-profit 1.1150 (150 pips reward) → RRR = 50 ÷ 150 = 1:3.
Read more:
- Topstep Trades Closed by What Time? Full Trading Hour Guide
- Forex Market Structure: Patterns, Tools & How to Read It
12. Conclusion: Master your formula for risk ratio, master your trades
By now, you’ve learned the core concepts of the formula for risk reward ratio, how to calculate it step-by-step, and how to apply it across various asset classes. More importantly, you’ve developed the mindset to protect your capital while maximizing gains.
Whether you're setting your first stop-loss or refining a seasoned strategy, let the risk/reward ratio be your compass. Use the tools, respect the math, and make every trade count.
Are you prepared to build a stronger base for your trading journey? Dive into the Forex Basics section on H2T Finance, where you’ll discover actionable tips, in-depth strategy guides, and expert insights, all designed to help you master the formula for risk ratio and apply it consistently in real trading conditions.



