Understanding the forex market structure is essential for any trader aiming to improve their trading skills and make informed decisions. The market structure forex provides a framework that reveals how price movements form patterns, where key support and resistance levels lie, and how different participants interact in the market.
In this guide, you will learn the basic market structure forex concepts, discover common forex market structure patterns, and find out how to read forex market structure effectively using popular charting tools. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced trader, mastering the forex trading market structure is a crucial step to enhance your strategy and manage risks better.
Let’s dive into the world of forex market structure and explore how to identify and leverage it for smarter trading.
Key takeaways:
- Forex market structure defines how prices move and how different players interact in the global currency market.
- The market is decentralized, but it follows repeatable patterns like trends, ranges, and price action cycles.
- There are three main forex markets: Spot (real-time trades), Forward (custom future contracts), and Futures (standardized on exchanges).
- Currency pairs are categorized into major, minor, and exotic pairs, each with unique liquidity and volatility traits.
- Understanding market structure helps traders identify trends, reversals, and key levels like support and resistance.
- Price structures include higher highs/lows, double tops/bottoms, and head & shoulders patterns.
- Platforms like MT4, MT5, and TradingView are essential tools for analyzing and visualizing structure effectively.
- Aligning strategy with structure, trend, range, or breakout improves timing and trade outcomes.
- Proper risk management uses structural zones (like recent highs/lows) to place stop-losses and size positions logically.
- Mastering market structure is a foundational skill for any serious forex trader.
1. What is the forex market structure?
The forex market structure refers to the way the global currency exchange system is organized from the hierarchy of participants to the flow of price action on the charts. Understanding this structure is crucial for traders who want to interpret price movements, time their entries and exits better, and build reliable strategies.

Unlike centralized markets such as stocks, the forex trading market structure is decentralized. This means there’s no single exchange or governing authority, and trades are executed over the counter (OTC) between parties across the globe. Still, despite this decentralized nature, the market follows identifiable patterns and behaviors that traders can learn to recognize.
At its core, the basic market structure forex traders follow includes concepts like trends, ranges, support/resistance, and price action cycles. These elements form the foundation of nearly every technical strategy, whether you're trading on MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), or using tools like TradingView.
By studying market structure forex, traders gain insight into the psychology behind price movements, allowing them to anticipate shifts in momentum and adapt their strategies accordingly. Whether you're just starting or refining your approach, mastering the forex market structure is a key step toward becoming a more confident and consistent trader.
2. Core components of forex market structure
The foreign exchange market is divided into three main components: the Spot Market, the Forward Market, and the Futures Market. Each type plays a distinct role and serves different participants from individual traders to large financial institutions.
2.1. Spot market
This is where currencies are bought and sold for immediate delivery at the current exchange rate. The spot market accounts for the majority of Forex activity and is where most retail traders operate.
Key characteristics:
- Immediate execution: Buy and sell orders are executed instantly at current market prices.
- Fast settlement: Typically settled within two business days due to time zone differences and banking processes.
- High liquidity: Especially for major currency pairs like EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY.
- Constant price fluctuations: Prices instantly reflect all news and economic events.
Tip: If you're a beginner or using short-term strategies like scalping or day trading, focus on the spot market — where you can execute trades and react to price changes in real time.
2.2. Forward market
In the forward market, parties agree to buy or sell a specific amount of currency at a set price for delivery on a future date. The exchange rate is locked in at the time the contract is made.

Key characteristics:
- Customized contracts: Terms like contract size and settlement date can be tailored to both parties’ needs.
- Hedging tool: Used by businesses and financial institutions to protect against future exchange rate volatility.
- No centralized exchange: Contracts are traded over-the-counter (OTC) directly between parties, not publicly listed.
Tip: If you're an import-export business or financial institution seeking to protect against unfavorable exchange rate moves, the forward market offers an effective way to stabilize costs and forecast profits. However, due to its highly personalized nature, it often lacks liquidity for retail investors.
2.3. Futures market
Similar to the forward market, but futures contracts are standardized and traded on centralized exchanges. This increases liquidity, transparency, and accessibility for a broader range of investors.
Key characteristics:
- Standardized contracts: Terms such as size and expiration date are predefined by the exchange.
- Organized trading: Takes place on centralized exchanges like CME, ensuring safety and transparency.
- Speculation & hedging tool: Suitable for professional investors seeking to use leverage to maximize returns.
- Strict risk controls: Includes mandatory margin requirements and risk management rules.
Tip: If you're an experienced investor looking to trade in a highly regulated environment, the futures market is an ideal choice. Its standardized structure and high liquidity also make it suitable for medium- to long-term trading strategies.
3. Types of currency pairs in the forex market: Major, minor, and exotic
In the foreign exchange market, currencies are always traded in pairs, known as currency pairs. Each pair consists of a base currency and a quote currency. The exchange rate indicates how much of the quote currency is needed to buy one unit of the base currency.
Example: If the EUR/USD pair is trading at 1.1000, it means you need 1.1000 USD to buy 1 EUR.
Based on popularity and liquidity, currency pairs are categorized into three main groups:
3.1. Major currency pairs
Major pairs are the most popular and widely traded currency pairs. They always include the US dollar (USD), which is the most powerful and liquid currency in the world. These pairs represent the most stable and developed economies.
Common examples:
- EUR/USD – Euro / US Dollar
- GBP/USD – British Pound / US Dollar
- USD/JPY – US Dollar / Japanese Yen
- USD/CHF – US Dollar / Swiss Franc
- AUD/USD – Australian Dollar / US Dollar
- USD/CAD – US Dollar / Canadian Dollar
- NZD/USD – New Zealand Dollar / US Dollar
Key features:
- High liquidity: Easy to buy/sell, fast execution, low spreads.
- Stable volatility: Price movements are often more predictable, suitable for a variety of trading strategies.
Tip: If you're a beginner, start with major pairs. They offer low spreads, are easier to analyze, and their high liquidity helps you manage risk more effectively.
3.2. Minor currency pairs
Minor pairs do not include the USD but consist of two strong currencies from major economies. They are also called cross-currency pairs.
Common examples:
- EUR/GBP – Euro / British Pound
- EUR/JPY – Euro / Japanese Yen
- GBP/JPY – British Pound / Japanese Yen
Key features:
- Moderate liquidity: Not as high as major pairs but still sufficient for retail traders.
- Higher volatility: Can offer greater profit potential, but also come with increased risk.
Tip: Trading minor pairs requires a deeper understanding of the relationship between the two economies. Be sure to study the fundamentals and technicals thoroughly before placing a trade.
3.3. Exotic currency pairs
Exotic pairs combine a strong currency (like USD or EUR) with a currency from an emerging market or developing country. These pairs tend to have low liquidity and high volatility.
Common examples:
- USD/TRY – US Dollar / Turkish Lira
- EUR/TRY – Euro / Turkish Lira
- USD/ZAR – US Dollar / South African Rand
Key features:
- High spreads: Due to lower trading volume, transaction costs are higher.
- Extreme volatility: Prices can swing rapidly due to economic instability, political risks, or local uncertainties.
Tip: If you choose to trade exotic pairs, make sure to have a strict risk management plan in place. They can offer big returns but can also wipe out your account in minutes if not handled properly.
4. How market structure affects your trading strategy
The structure of the Forex market plays a crucial role in shaping the most suitable trading strategy. Understanding each market segment and currency pair type allows you to choose an approach that aligns with your goals, trading timeframe, and risk tolerance.
Here’s how market structure can influence your trading strategy:
- Spot market: Ideal for scalping and day trading thanks to high liquidity and instant order execution. Best suited for short-term trades that respond quickly to news and market volatility.
- Forward and futures markets: More suitable for long-term strategies or institutions aiming to hedge against future exchange rate fluctuations. These markets prioritize stability over short-term gains.
- Currency pair selection:
- Major pairs offer a safer choice for beginners due to their low spreads and more predictable price movements.
- Minor and exotic pairs are better suited for traders seeking higher risk–reward opportunities, but they require experience and strong analytical skills.
Additionally, understanding market structure helps improve price movement forecasts.
For example: If you know a central bank is likely to intervene, you can anticipate sharp price movements around monetary policy announcements and prepare accordingly.
5. Who moves the market? Key participants in forex
Behind every price movement in the forex market lies the action of its key players. Understanding who moves the market helps traders anticipate shifts in supply and demand, sentiment, and volatility - all essential to interpreting basic market structure forex.
While millions of individual traders participate daily, the true power lies with a few dominant groups whose transactions drive the global currency ecosystem.
5.1. Banks and financial institutions
Major commercial and investment banks are the largest participants in the forex market. Through interbank trading, they provide the majority of liquidity in the forex market structure. Their actions are typically based on client orders, institutional hedging, or proprietary trading strategies.
Because of their size and speed, banks can cause significant price fluctuations, often triggering structural shifts such as breakouts or trend formations that retail traders seek to capitalize on.
5.2. Central banks
Central banks influence currency markets through monetary policy, interest rate decisions, and direct intervention. Their goal is to stabilize their nation's economy, but their actions frequently reshape the forex trading market structure.
For example, unexpected rate hikes or quantitative easing can lead to long-term trend reversals or strengthen existing market structure patterns. Keeping track of central bank calendars and statements is crucial when learning how to identify market structure in forex.
5.3. Multinational corporations
Global companies engaging in cross-border trade and investment generate large-scale forex transactions. While not primarily speculative, these flows impact supply and demand, especially in key currency pairs.
Understanding how corporations hedge currency risk often through the forward or futures markets can provide insights into longer-term structural trends.
5.4. Retail traders & speculators
Retail traders are the smallest group in terms of volume but the largest in number. Armed with platforms like MT4 and TradingView, they trade the spot market using technical patterns and tools.
Though they don’t move the market alone, their collective behavior contributes to common forex market structure patterns such as false breakouts, consolidation zones, and support/resistance reactions.
6. Understanding forex market structure patterns
Recognizing price patterns is the foundation of reading and interpreting the forex market structure. These patterns reveal the underlying forces of supply and demand, trend strength, and potential reversal points helping traders make informed decisions and time their entries more effectively.
By understanding how market structure evolves, you can develop an edge in identifying opportunities, managing risk, and adapting to shifting market conditions.
6.1. Trend structures – higher highs & higher lows
A trending market creates a clear structural rhythm: in an uptrend, price forms higher highs (HH) and higher lows (HL); in a downtrend, it produces lower lows (LL) and lower highs (LH).
This sequence defines the basic market structure forex traders rely on to confirm the trend’s direction and strength. When the sequence is broken such as a lower low in an uptrend, it may signal a potential reversal or consolidation.
Mastering this concept is essential when learning how to read forex market structure, as trend identification is the core of most strategies.
6.2. Reversal structures – double tops, head & shoulders
Reversal patterns form when the existing trend loses momentum. Common formations include:
- Double tops and bottoms: Price tests a level twice, failing to break through, signaling a possible shift.
- Head and shoulders / Inverse head and shoulders: A classic structure indicating a change in trend direction, often followed by strong moves.
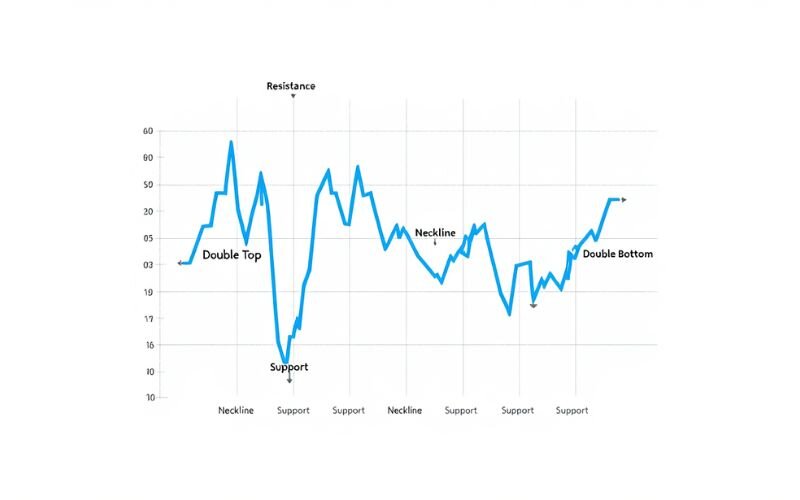
These forex market structure patterns offer early warnings of a potential reversal. Spotting them on higher timeframes can give added confluence to your entries on lower charts.
6.3. Support & resistance – structural pillars
Support and resistance levels are critical to market structure. They often align with swing highs/lows and key psychological levels, acting as decision zones for both institutions and retail traders.
- Support: A level where demand prevents price from falling further.
- Resistance: A level where supply caps further price increases.
These zones create the framework for price movement, acting as pivots in structure. Tracking them helps you identify market structure in forex more accurately.
7. How to read forex market structure with charting tools
Learning how to read forex market structure effectively starts with mastering your charting tools. These platforms help you visualize price movements, draw structure zones, and analyze key swing points - all crucial for building reliable strategies.
Whether you’re trading on short-term or long-term timeframes, understanding market structure visually allows you to anticipate price behavior instead of reacting to it.
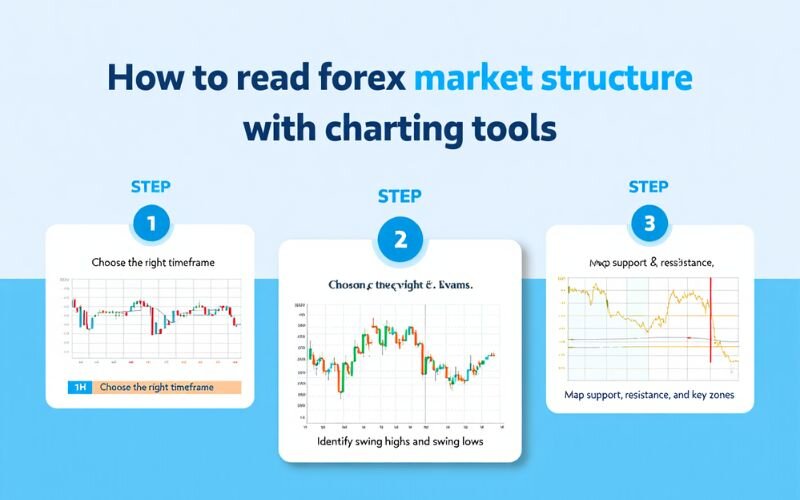
Here’s a step-by-step guide to identifying structure on your charts.
Step 1: Choose the right timeframe
- Start with a higher timeframe (daily or H4) to identify the broader trend and major structural levels.
- Then move to a lower timeframe (H1, M15, M5) for precise entries, exits, and risk placement.
- Structure forms at all timeframes, but higher timeframes tend to be more reliable.
This top-down approach allows you to identify market structure in forex with better accuracy and confluence.
Step 2: Identify swing highs and swing lows
- Swing high: A peak where price reverses downward.
- Swing low: A trough where price turns upward.
By connecting these points, you can track the trend: HH/HL in uptrends, LL/LH in downtrends. Look for breaks in structure (BOS) and change of character (CHOCH) to anticipate possible trend shifts.
Step 3: Map support, resistance, and key zones
- Use horizontal lines or rectangles to highlight support and resistance levels.
- These act as structural zones - areas where price often reacts or consolidates.
- Combine structure with volume or momentum indicators (like RSI or MACD) to add confirmation.
For quick reference, many traders build a forex market structure cheat sheet that summarizes trend and reversal patterns, ideal for backtesting or training.
Tip: Use the “line chart” view to clearly see swing points without candlestick noise.
Reading structure is not just about memorizing patterns, it’s about understanding market behavior. Over time, this skill becomes a core pillar of any profitable trading strategy.
See more related articles:
- Topstep Trades Closed by What Time? Full Trading Hour Guide
- What is forex exchange trading? Explained for total beginners
- What is a trailing stop order? Smart risk control 2025
8. Best platforms to analyze market structure: MT4 vs MT5 vs TradingView
To analyze the forex trading market structure effectively, having the right platform is just as important as knowing the theory. The right charting software enables you to identify trends, draw zones, test strategies, and stay alert to market changes all in real-time.
Let’s compare three of the most popular tools among forex traders: MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), and TradingView.
Overview before comparison: Each platform has its strengths depending on your trading style. While MT4 and MT5 are widely used for execution and expert advisors (EAs), TradingView shines for its powerful visuals, community scripts, and seamless multi-device support.

The table below breaks down key features across platforms:
| Feature | MT4 | MT5 | TradingView |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charting Tools | Basic but sufficient | Advanced (more timeframes) | Highly advanced & intuitive |
| Execution Capability | Broker-linked | Broker-linked | No execution (charting only) |
| Custom Indicators | Yes (MQL4) | Yes (MQL5) | Yes (Pine Script) |
| Strategy Testing | Built-in backtesting | Multi-threaded tester | Manual backtest only |
| Usability on Mobile/Web | Moderate | Good | Excellent |
| Community & Social Features | Limited | Limited | Large active community |
Which platform is best for analyzing market structure?
- Use MT4 if you’re a beginner or trading with a broker that only supports MT4. It covers the basic market structure forex needs with enough charting tools for trend and support/resistance analysis.
- Use MT5 if you want deeper analytics, access to more symbols and timeframes, and multi-asset support.
- Use TradingView if you’re a structure-based trader who values precision, visual clarity, and community ideas. Many traders build and share forex market structure patterns on TradingView, making it a great learning environment.
Each of these platforms can help you learn how to identify market structure in forex, especially when paired with a clear system for marking trends, breakouts, and key zones.
Tip: Try combining MT5 for order execution with TradingView for structure analysis. You get the best of both worlds.
9. Aligning strategy with market structure
Recognizing the forex market structure is only the first step. The next is learning to align your trading strategy with what the structure is telling you. Whether the market is trending, ranging, or breaking out of consolidation - your edge comes from trading with the structure, not against it.
In this section, we’ll explore how to match popular trading strategies to different market structure forex conditions.
9.1. Trading with the trend
When the market forms higher highs and higher lows in an uptrend, or lower highs and lower lows in a downtrend, it signals a trending market. This is when structure-based trend trading thrives.
Key tactics:
- Buy pullbacks to support in an uptrend or sell rallies to resistance in a downtrend.
- Use tools like moving averages, Fibonacci retracements, or trendlines to time entries.
- Confirm entries with structure shifts on lower timeframes.
Trend trading aligns naturally with the basic market structure forex offers. It minimizes false signals by focusing only on strong directional flows.
9.2. Range-bound strategies
Not all markets trend. When price oscillates between defined support and resistance, you’re in a range - a sideways structure.
How to trade ranges:
- Identify horizontal levels where price consistently reverses.
- Buy near support and sell near resistance with tight stop-losses.
- Use oscillators like RSI or Stochastic for overbought/oversold signals.
This environment suits patient traders who wait for price to “ping-pong” within levels. Understanding how to read forex market structure in ranges prevents unnecessary trades during choppy conditions.
9.3. Reversal & breakout trading
Once a trend or range ends, the market often shows forex market structure patterns like double tops/bottoms or head and shoulders, signals of potential reversal or breakout.
Structure-based breakout strategies:
- Watch for break of structure (BOS) beyond previous swing highs/lows.
- Confirm the move with volume or retest of broken zones.
- Target new trend legs, using structure as a guide for trailing stops.
Reversal trading requires more confirmation but can offer excellent risk-reward. A solid understanding of how to read forex market structure helps traders catch early signs of shift before most others react.
Tip: Match strategy to structure first. Trying to trend trade in a range or vice versa is one of the top reasons traders lose money.
10. Risk management and market structure
In forex trading, understanding forex market structure is essential not just for finding entry points but also for managing risk effectively. The market’s structure helps traders identify logical areas to place stop-loss orders and define their risk zones clearly.
Using structure for stop-loss placement: A well-placed stop-loss is often set just beyond key market structure forex levels, such as recent swing highs or lows. For example:
- In an uptrend, place stops just below the most recent higher low to protect against unexpected reversals.
- In a range, stops go just outside the support or resistance zone boundaries.
- When trading breakouts, stops can be set below the breakout candle or the retest level of the broken structure.
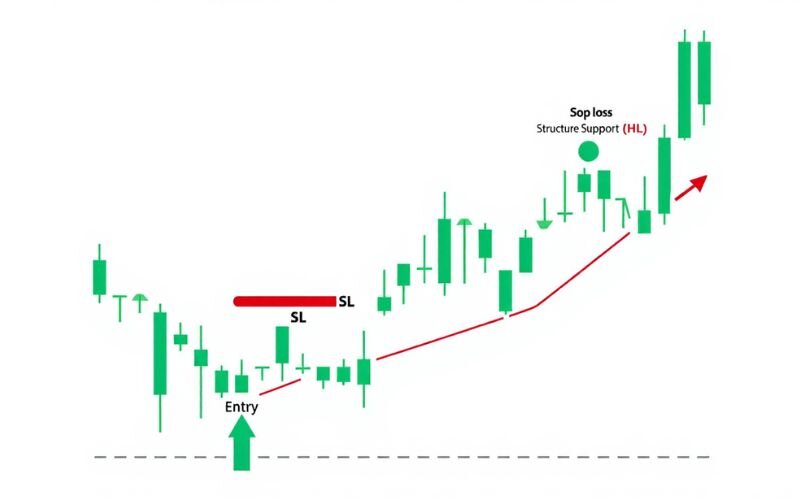
This method leverages the natural forex trading market structure to keep risk tight while allowing the trade room to breathe.
Position sizing according to structure: By knowing your stop-loss distance relative to the structure, you can calculate your position size to control risk percentage per trade. This systematic approach helps avoid emotional trading and unexpected losses.
Managing risk during volatile structure shifts: Major forex market structure patterns, such as reversals or strong breakouts, often bring increased volatility. Traders should:
- Reduce position sizes during uncertain or choppy market conditions.
- Avoid entering trades when structure signals conflict.
- Use trailing stops aligned with new structure lows/highs to lock in profits.
Proper risk management combined with a clear grasp of how to identify market structure in forex enhances trading consistency and long-term success.
Read more: What is a stop limit order? How does it work, and when to use it?
11. FAQs – Frequently asked questions about forex market structure
11.1. What is Forex market structure?
Forex market structure refers to the organization of the foreign exchange market, including price behavior, support/resistance levels, and the roles of market participants. Understanding this structure helps traders identify trends, entry/exit points, and manage risks more effectively.
11.2. Why do traders need to learn how to read market structure?
Because it helps traders understand market flow, spot reversal signals, and determine optimal trading moments. It serves as the foundation for building a strategic trading edge.
11.3. Which timeframe does market structure apply to?
Market structure appears on all timeframes. However, higher timeframes like H4 or Daily are generally more reliable for identifying the primary trend.
12. Final thoughts: why understanding structure gives you an edge
Grasping the forex market structure is a fundamental skill that sets successful traders apart. By learning how to read forex market structure, you gain clarity on market direction, key support and resistance levels, and potential reversal points. This knowledge transforms the way you analyze charts and make trading decisions.
Understanding market structure also helps you align your strategies more effectively, whether you prefer trend-following, reversal, or range-bound approaches. Coupled with proper risk management, it gives you a robust framework to navigate the complexities of the forex market.
At H2T Finance, we believe that mastering the core principles of market structure forex empowers you to trade with confidence and discipline. Take time to study patterns, use the right tools like MT4, MT5, or TradingView, and always respect the signals the market gives through its structure.
For those starting out or wanting to deepen their knowledge, don’t miss our comprehensive Forex Basics category, where you can find essential guides and resources to build a strong foundation in forex trading.
By doing so, you’re not just guessing, you’re trading with a strategic edge.



